Akansha Sharma 2025-09-22
Walk into any modern building, pick up a running shoe, or unwrap a fragile delivery item, chances are you’re holding the invisible work of blowing agents. These substances quietly transform heavy, rigid materials into lightweight, insulating foams. They are the reason why packaging cushions delicate goods, and buildings stay cooler in summer.
But how do they actually work? Let’s explore.
In simple terms, a blowing agent is a substance that generates gas within a material, usually a polymer causing it to expand and form a cellular structure. Think of it as “bubbling up” the material from the inside. Once cooled or cured, those bubbles remain trapped, creating a foam.
This foamed structure drastically reduces weight, enhances insulation, and can even change the material’s flexibility or strength. From construction to footwear, blowing agents are behind some of the most versatile materials of our time.
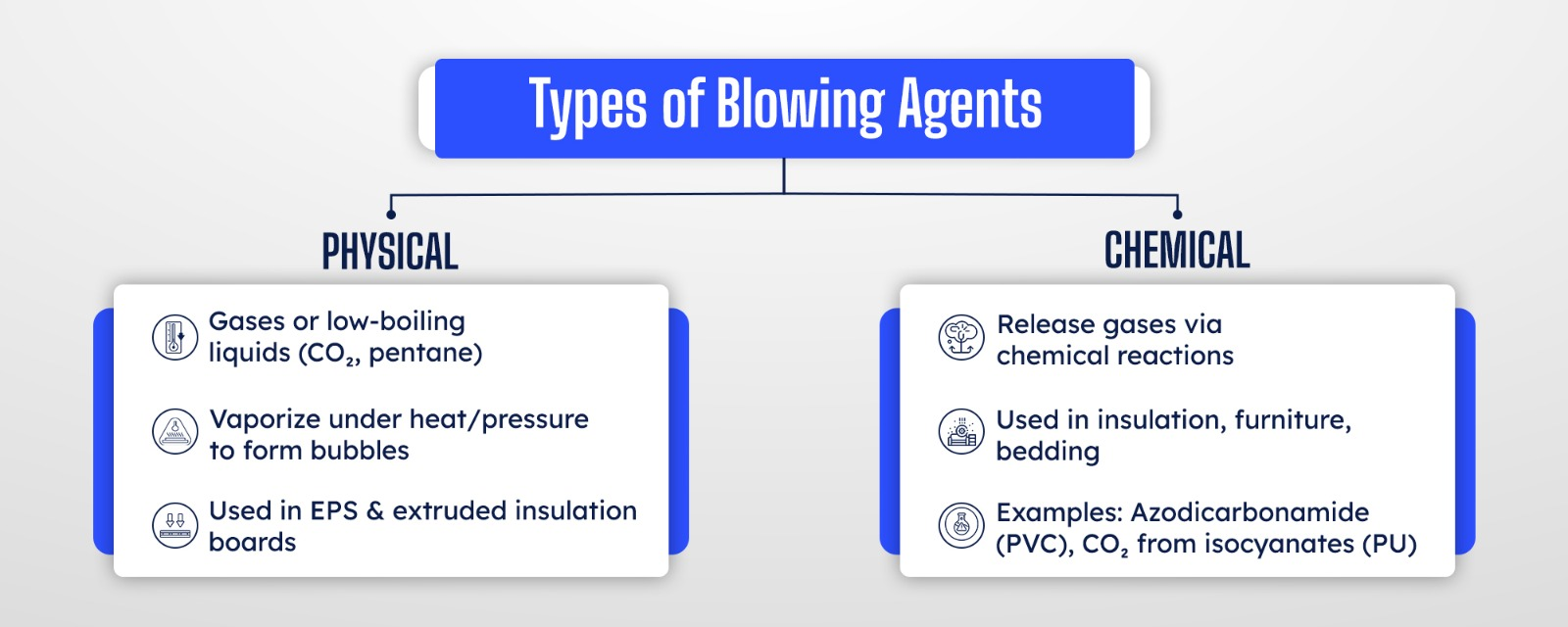
Some industries also use hybrid or mixed systems, combining both approaches for finer control over foam density, expansion rate, and thermal performance.
The foaming process begins with nucleation, the formation of tiny gas bubbles in the molten polymer. These bubbles grow as more gas is released or vaporized, pushing the material outward. Factors like polymer viscosity, surface tension, and temperature determine whether bubbles remain stable or collapse.
Once cooled or cured, the material locks into place, creating either closed-cell foams (good for insulation, moisture resistance) or open-cell foams (softer, breathable, cushioning).
This delicate balance between chemistry and physics is what makes foamed products so versatile.
Why Foams Matter: Lightweight and Insulating
At the heart of foamed materials is one simple truth: air is an excellent insulator. By trapping gases inside their cellular structures, foams slow down heat transfer dramatically. That’s why polystyrene boards keep houses warm, or why packaging foams protect frozen food.
Key benefits include:
A Subtle Shift Towards Sustainability
The science of blowing agents hasn’t stood still. Earlier generations like CFCs and HCFCs were phased out due to ozone concerns. Even HFCs, though ozone-safe, have been curbed for their high global warming potential.
Today, innovation is driving toward low-GWP alternatives—hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs), hydrocarbons, and even bio-based options. The aim is clear: keep the benefits of foamed materials while reducing environmental footprint.
Expancel® Microspheres: A Smarter Blowing Agent
This pursuit of smarter, lighter, and more efficient materials has also led to innovations like Expancel® microspheres. Unlike traditional blowing agents, these tiny thermoplastic beads have a gas-filled core. When heated, their shell softens, and the gas expands, making the microspheres increase in volume up to 60–80 times.
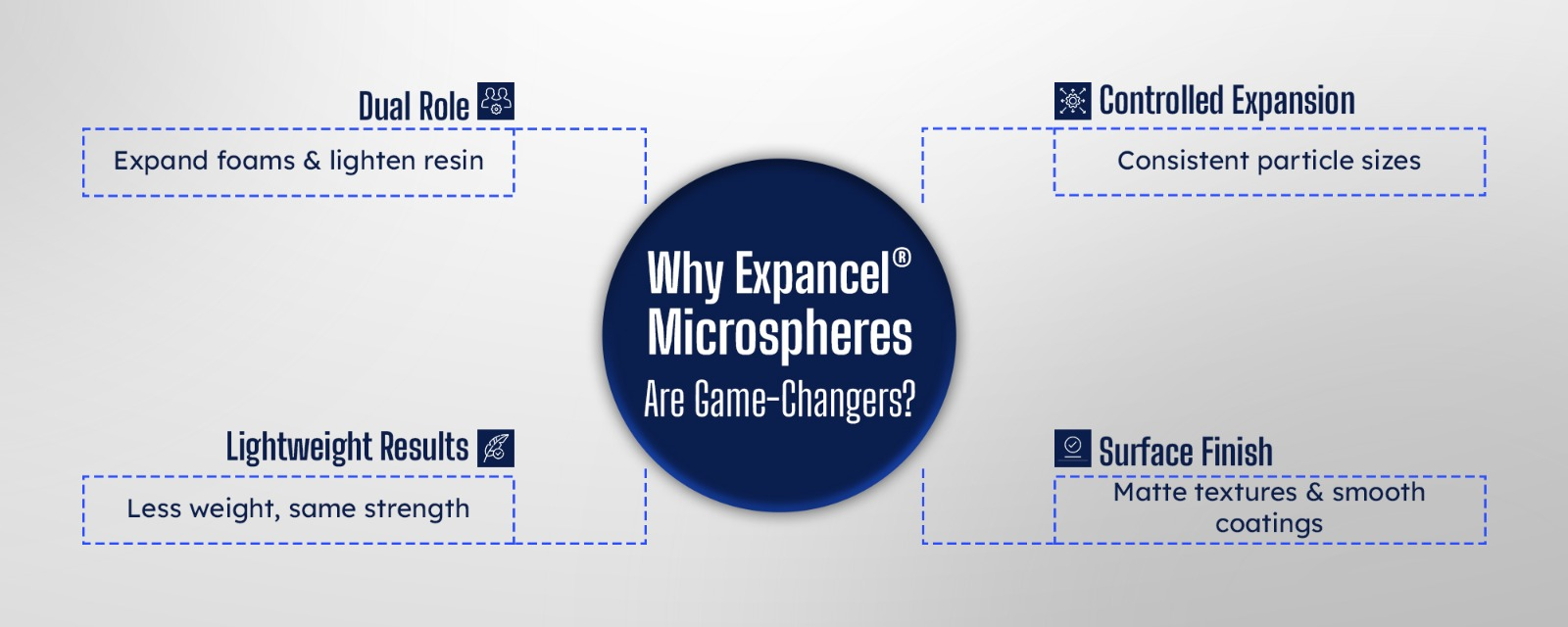
Applications range from footwear soles, sealants, and packaging foams to automotive parts and specialty coatings. Rajshila’s partnership with Nouryon brings these advanced materials closer to Indian manufacturers seeking efficiency and performance.
Industries Transformed by Blowing Agents
The Future of Lightweight and Insulating Materials
From the bubbles that make packaging protective, to the foams that keep buildings cool and shoes comfortable, blowing agents continue to define how we design for strength, efficiency, and comfort. And as industries move toward greener solutions, innovations like Expancel® microspheres show how performance and sustainability can work together.
At Rajshila, we’ve spent decades helping industries adopt smarter materials, from traditional foams to advanced solutions like Nouryon’s Expancel® microspheres. Our role is to ensure manufacturers don’t just keep pace with change, but lead it, building products that are lighter, stronger, and better insulated for the future.
If you’re looking to innovate with foams and insulating materials, partner with Rajshila to explore solutions that make every product smarter.
Read more: What are blowing agents and why are they used in foam products?
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blowing_agent?utm_
https://www.haltermann-carless.com/blog/physical-blowing-agents-the-role-of-pentane-quality-for-insulation-materials?utm
https://www.specialchem.com/plastics/guide/expanded-polystyrene-eps-foam-insulation?utm
https://www.fluorocarbons.org/applications/insulation-foam-blowing-agent/
https://www.nouryon.com/products/expancel-microspheres/
https://rajshila.com/blog/Tiny-Spheres-Big-Innovation-How-Expancel-Microspheres-Revolutionize-Manufacturing